Addiction is a complex condition characterized by persistent, compulsive dependence on a substance despite harmful consequences. Many substances have the potential to be addictive, but some stand out due to their high potential for abuse and dependency.
According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), 48.7 million people aged 12 or older had a substance use disorder during 2021 – including 29.5 million with alcohol use disorder.
Understanding which drugs are the most addictive can help in forming strategies for prevention and treatment. Explore some of the most addictive drugs, examining their effects on the body and mind, and determine which ones are the most addictive in the country.
The Most Addictive Drug
Determining the most addictive drug is challenging due to the different ways substances affect individuals. However, considering the intensity of the addiction, the rapid onset of dependency, and the severe withdrawal symptoms, heroin is often regarded as the most addictive drug. Its profound impact on both the mind and body, coupled with the difficulty in overcoming addiction, places it at the top of the list – but there are several other substances that give heroin stiff competition.
Heroin
Heroin, an opioid derived from morphine, is often cited as one of the most addictive drugs. Its high addiction potential is attributed to the rapid onset of euphoria it produces. When injected, heroin reaches the brain quickly, creating intense feelings of pleasure and well-being. This immediate and profound effect is due to the drug’s ability to bind to and activate opioid receptors in the brain, which regulate pain and reward.
The addiction to heroin is not only psychological but also physical. Regular use leads to tolerance, meaning users need increasingly larger doses to achieve the same effect. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and include muscle and bone pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and cold flashes, making it extremely difficult for users to quit without professional help.
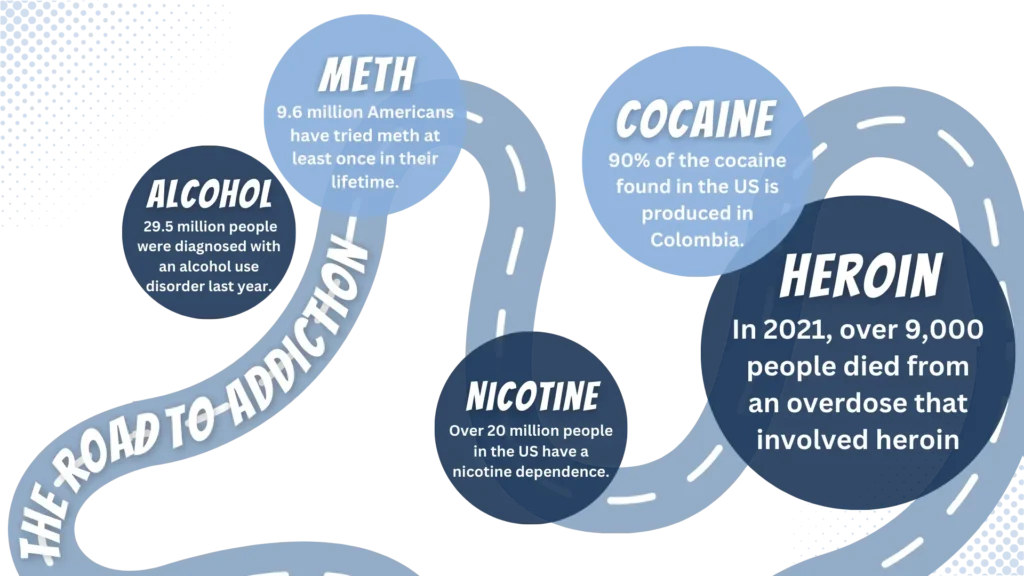
In 2021, approximately 9,173 people died from an overdose that involved heroin.

Cocaine
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that increases levels of dopamine in the brain, leading to heightened alertness, energy, and intense feelings of euphoria. Its addictive nature stems from its ability to interfere with the brain’s reward pathways, making users crave more of the drug to replicate the pleasurable sensations.
Cocaine addiction can develop quickly, even after just a few uses. Users often binge on the drug, taking it repeatedly over several hours or days, which can lead to severe health consequences including heart attacks, strokes, and neurological issues. The psychological dependence on cocaine is profound, with intense cravings and the need to use the drug to feel normal.
Approximately 90% of the cocaine found in the United States is produced in Colombia.
Nicotine
Nicotine, found in tobacco products, is one of the most widely used addictive substances in the world. It stimulates the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, providing a pleasurable and calming effect. Despite being legal and widely available, nicotine is highly addictive, with many users finding it extremely difficult to quit.
The addictive nature of nicotine is partly due to its rapid absorption and the quick onset of its effects. Smoking a cigarette delivers nicotine to the brain within seconds, reinforcing the behavior. Nicotine withdrawal can lead to irritability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and intense cravings, which are major barriers to quitting.
According to the NSDUH, approximately 23.6 million people had a nicotine dependence in 2021.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, is a potent central nervous system stimulant that causes increased activity, decreased appetite, and a sense of euphoria. Meth is highly addictive, primarily due to its powerful effects on the brain’s reward system. It releases a surge of dopamine, far greater than the amount naturally produced, leading to intense pleasure.
Chronic use of methamphetamine can lead to severe psychological and physical issues, including anxiety, confusion, insomnia, mood disturbances, and violent behavior. Long-term use can also result in significant brain damage, affecting memory and cognitive function. The intense cravings and harsh withdrawal symptoms, including fatigue, depression, and increased appetite, make methamphetamine one of the hardest addictions to overcome.
A study on methamphetamine use uncovered that an estimated 9.6 million Americans age 12 and older has used methamphetamine at least once in their lifetime.
Alcohol
Alcohol is another widely consumed substance with a high potential for addiction. It acts as a central nervous system depressant, producing effects such as relaxation, reduced inhibition, and euphoria. Regular, heavy use of alcohol can lead to dependence and addiction.
Alcohol addiction, or alcoholism, is characterized by a strong craving for alcohol, loss of control over drinking, and withdrawal symptoms when not drinking. These symptoms can include tremors, anxiety, nausea, and in severe cases, seizures. The social acceptability and availability of alcohol contribute to its widespread abuse and the challenges associated with treating alcoholism.
According to the 2022 NSDUH, 29.5 million people ages 12 and older had an alcohol use disorder diagnosed in the past year.
Prescription Opioids
Prescription opioids, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, and fentanyl, are often prescribed for pain relief but have a high potential for addiction. These drugs work similarly to heroin by binding to opioid receptors in the brain, producing pain relief and euphoria.
Misuse of prescription opioids can quickly lead to dependence and addiction. Tolerance develops, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect, and withdrawal symptoms can be severe. The opioid crisis in many parts of the world highlights the dangers of these medications, which, while medically beneficial, carry a significant risk of addiction.
Approximately 600,000 deaths worldwide are attributed to drug use – 80% of them are attributed to opioid use.
Crack Cocaine
Crack cocaine, a freebase form of cocaine that can be smoked, is extremely addictive. Smoking crack allows the drug to reach the brain quickly, producing an intense and immediate euphoria. This rapid onset makes crack cocaine more addictive than powdered cocaine.
The addiction to crack cocaine is characterized by an intense craving for the drug, often leading to compulsive use. The short duration of its high causes users to take the drug repeatedly in a short period, increasing the risk of addiction and severe health issues. The social and economic consequences of crack addiction are profound, often leading to severe personal and societal problems.
According to the National Household Survey on Drug Abuse, an estimated 6,222,000 people aged 12 and older reported using crack cocaine at least one time in their lives.

Conclusion: Seeking Treatment From The Most Addictive Drugs
Understanding the addictive potential of various substances is crucial in addressing the global issue of drug addiction. Heroin, cocaine, nicotine, methamphetamine, alcohol, prescription opioids, and crack cocaine each have unique properties that make them highly addictive. Efforts to combat addiction must focus on prevention, education, and comprehensive treatment strategies to help those affected regain control over their lives.
Heroin stands out due to its immediate and intense effects, severe withdrawal symptoms, and the high likelihood of addiction.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction regarding these or any substances – reach out to Southeastern Recovery Center to learn more about our addiction treatment programs.